What is User Experience?
User Experience focuses on obtaining a deeper understanding of what your customers need and value and cultivating knowledge about their abilities and limitations.
A positive user experience promotes and improves the quality of the user’s interaction, as well as shaping how your products and services perform.
User Experience Honeycomb
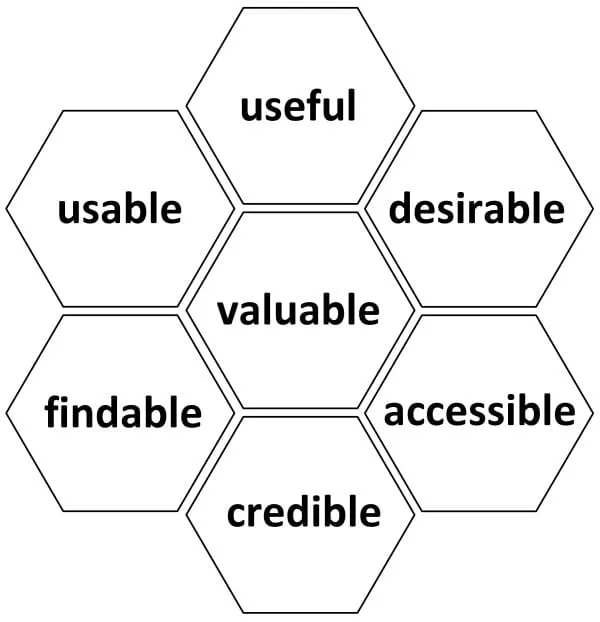
Peter Morville represents the core of User Experience through the UX Honeycomb. In order to have meaningful and relevant experiences, information must be offered as follows:
1. Useful
We all know the impact of content. In order to keep your customers, your use of words should be original and fulfill a need.
Keep in mind that the customers that browse your website find value, which has led them to you.
2. Usable
User Experience layout should be easy to use. Your customers want an easy-to-navigate website.
With an easy-to-use feature, your customers will be able to click on buttons, scroll, and find the content they need or want.
3. Desirable
Desire is something that people have within, however, the way something or someone is presented plays a large role.
Regarding your site, it is important to include brand identity, images, and other visual design elements to evoke emotion as well as appreciation.
4. Findable
With a useful, easy-to-use, navigable site that allows your customers to locate products and services onsite as well as offsite, you would have hooked your customers.
5. Accessible Design
Your content should be accessible to people with disabilities. An example could be the use of alt texts, keyboard navigation, and transcripts.
6. Credible
To have loyal and committed customers, they need to feel that they can trust what you are promoting and the information you are sharing with the world.
Having cited reliable sources supporting your claims and leaving feedback and reviews elevates your credibility.
Building User Experience
To successfully create a user-centered design, the principles of human-computer interaction go further and include the following disciplines:
| Topic | Description |
|---|---|
| Project Management | The graphic designer should be capable of identifying, managing, and applying the lifecycle to the user-centered design process to form the project team, guide them through all phases, and reach completion. |
| User Research | Research plays a vital role in understanding your audience. Through observation techniques and other feedback methodologies, you will formulate a website layout that appeals to your customers. |
| Usability Testing | User evaluation or testing focuses on how well users can adapt to using your product or services to achieve their goals. It also assesses if you successfully satisfy customers with that process. |
| Information Architecture | Information architecture refers to how information is organized, structured, and presented to your users, much like architecture has a foundation, wood, then concrete. |
| User Interface Design | Anticipate users’ needs and ensure the interface has easily accessible, understandable elements that facilitate the required actions. |
| Visual Design | UX designers ensure an aesthetically pleasing interface that aligns with brand goals and identity. The design process is as important as the foundation or infrastructure. |
| Content Strategy | Plan, create, design, and govern written and visual content. A content strategy ensures the website’s content is coherent and effective. |
| Accessibility | Ensure your website is accessible to everyone, including disabled individuals, focusing on how they will access or benefit from your site. |
| Web Analytics | Track, collect, report, and analyze website data to identify faults and improvements, updating your website accordingly. |
User-Focused vs Pixel-Focused
User-Focused is an approach that focuses on the needs, preferences, and behaviors of users, making them the focal point.
Pixel-Focused design is an approach emphasizing the the visual details of a design. The placement, size, and color of elements—the aesthetics—are known as pixel-focused.
UX Deliverables
A summary of the findings from research done to better understand the requirements, preferences, and behaviors of users is presented in a user research report.

User Personas
A representation of the many user types that the design should take into account Personas often include information such as age, gender, occupation, goals, and pain areas and are based on research data.
A user journey customer map is a visual representation of a user’s interaction with a product or service over time. It can aid designers in better understanding user requirements and pinpointing areas for development.
Information architecture refers to how a product’s content and features are organized and structured. It aids consumers in finding what they seek and achieving their objectives.
Basic, low-fidelity sketches of a design’s content and layout are called wireframes. They assist designers in investigating various layouts
UX Design Tools
UX designers use software applications and programs to create prototypes of user interfaces and user experiences.
These UX design tools assist UX designers through the creation of wireframes, mockups, and interactive prototypes for websites, apps, and more.
Other examples of UX design tools are:
UX Design Disciplines: The Quadrant Model
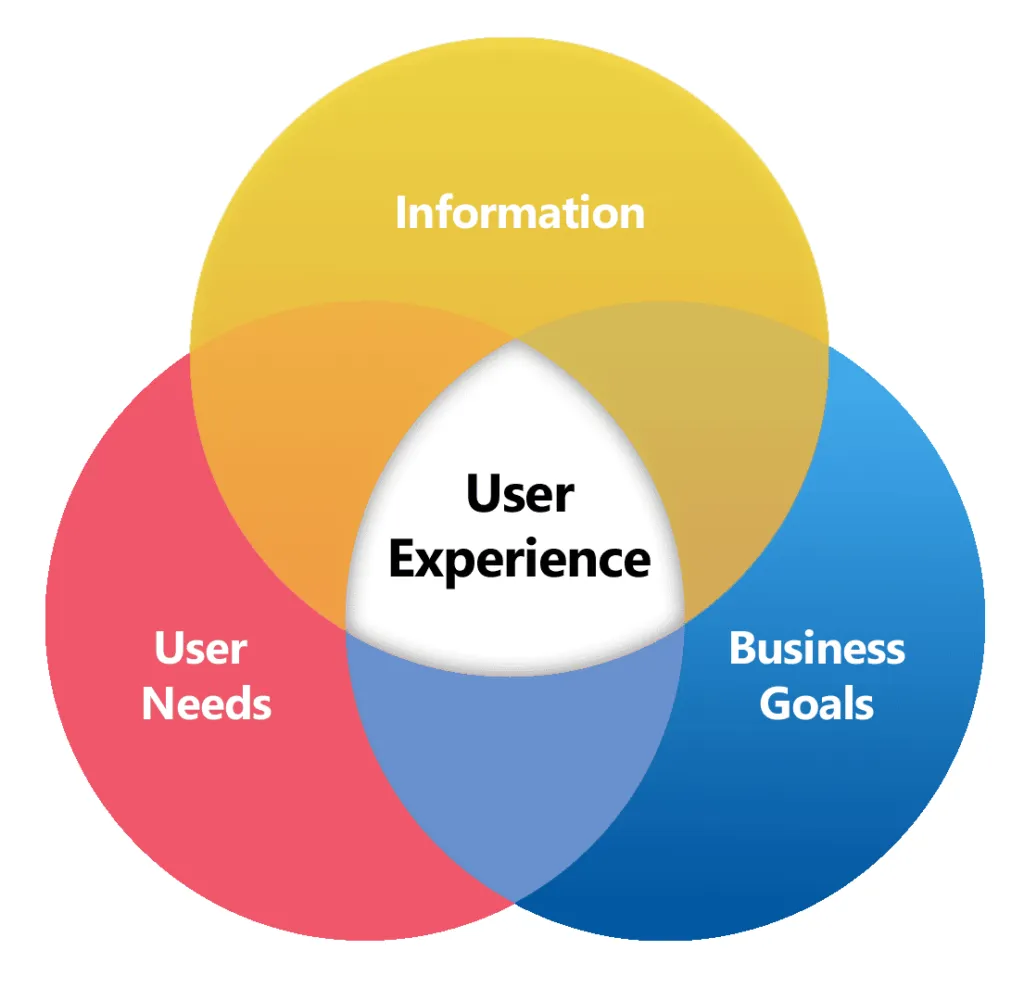
A framework that assists designers in organizing and understanding the different disciplines, the Quadrant Model represents different areas of focus, such as:
- User Research
- Information Architecture
- Interaction Design
- Visual Design
Useful in many ways, the Quadrant Model provides a useful guide to understanding the different sectors in UX Design.
By offering sufficient focus on each quadrant, UX designers can create products and services sufficient for user needs.
What is User Interface Design?
User Interface, or UI, is the process of designing the visual and interactive elements that go into the digital product.
More often than not, UI and UX designers work hand-in-hand or are the same person, being responsible for creating the look and feel, layout of the elements on the screen, color scheme, typography, and imagery, as well as the behavior of how elements tend to interact together.
A perfected UI design is essential to creating products and services that are not only functional but are also visually pleasing and engaging to offer customers increased user satisfaction and brand loyalty.
The Difference Between UX and UI Design
UI design has more to do with the look and feel of the digital product and services as opposed to UX, which has more to do with the overall user experience.
They are related and demand to be worked on closely; they require different skill sets and approaches.
Interaction Design (IxD)
UI and UX are important factors; another important factor is IxD, which is the ability to create an intuitive and efficient user experience with clear feedback and a logical flow of tasks.
IxD Designers focus on designing the behavioral aspects of interactive elements such as buttons, menus, forms, layouts, and navigation.
IxD designers must ensure that the design is not only accessible but usable by all people, whether they have disabilities or are in need of assistive technologies.
Key Questions UX Designers Ask Themselves
It is important that UX Designers ask questions to help keep in mind certain tools and considerations, such as User Flow and User Testing.
Some of the questions the UX designers might continuously go over and consider are the following:
- Who are the users of the product?
- What are the users’ goals and needs?
- How can the user experience be improved?
Company Size Determines the Scope of What a UX Designer Does
The size of the company can have an influence on what UX designers are capable of. In larger companies, UX designers may specifically specialize in a particular aspect of UX design, such as research or interaction design.
In smaller companies, UX designers may be required to handle more than one aspect of the UX design process, which would include research, prototyping, and user testing.
Regardless of the size, the goal that befalls UX designers is to create products and websites that meet user needs and ensure a positive user experience.
Effective communication, attention to detail, and a focus on user-centered design are all important qualities that UX designers should hone.

Usability Testing Tools
UX designers have many tools that allow effective testing. Testing tools offer UX designers the chance to receive feedback from real users, which is recorded and analyzed. This helps UX designers cultivate a much more enriched understanding of user behavior.
Some of these tools are:
Keep in mind that each tool has its own strengths and limitations, which is why it’s up to the UX designer to choose the best fit for their needs and, most importantly, the needs of their users.
Create User Personas
Keep in mind that in order to best understand your customers, you need to create a buyer persona that helps you better shape your targeted audience.
The design thinking process needs to be aligned with the buyer persona since that will, therefore, help the sales and marketing teams generate content that will be sent to potential leads via email marketing or even on social media.
Create more than one user persona to have a competitive advantage and reach. We understand the limitations of physical interaction over the internet, and that is the main target of UX designers:
To offer customers a place where people interact and gain an entire process of augmented reality that is a blend of digital content with the real world.
User Experience
User experience is a critical component of the design process for websites, apps, and other digital products or services.
What leads to a more positive user experience is the UX designer’s understanding of user needs and behaviors to create user personas through psychological and behavioral skills as well as technical skills in design tools and technologies.
Our Guru Designers implement the understanding and use of User Experiences and User interfaces to create a website that is easy to navigate through hierarchies while maintaining brand essence.
Join the GuruDesk community and be among the first ones to discover the hottest trends in web services! We are a team of web experts and we love sharing our knowledge and experience with our readers! We share tips and tricks on a wide range of topics, including web development, cloud services, and hosting. Whether you are a seasoned pro or just starting out, we promise you will find valuable information here. So go ahead, hit that “Subscribe” button and let the fun begin!






